Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2022-071, 123 Pages, 2023/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of a hybrid method for evaluating the long-term structural soundness of nuclear reactor buildings using response monitoring and damage imaging technologies" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to develop an evaluation method necessary to obtain a perspective on the long-term structural soundness of accident-damaged reactor buildings, where accessibility to work sites is extremely limited due to high radiation dose rate and high contamination. In FY2021, the first year of the three-year plan, the following research items were undertaken by clarifying specific research methods, setting research directions, making necessary preparations, and conducting some tests and other activities.
Planning and Co-ordination Office, Sector of Nuclear Safety Research and Emergency Preparedness
JAEA-Evaluation 2022-008, 68 Pages, 2022/11
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) consulted an assessment committee, "Evaluation Committee of Research and Development (R&D) Activities for Nuclear Safety Research", for post-review and pre-review assessments of Nuclear Safety Research, in accordance with "General Guideline for Evaluation of Government R&D Activities" by Cabinet Office, Government of Japan, "Guideline for Evaluation of R&D in Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology" and "Regulation on Conduct for Evaluation of R&D Activities" by JAEA. In response to the JAEA's consult, the Committee assessed the results and outcomes of the R&D programs during the 3rd mid-/long-term plan (from April 2015 to March 2022, including the expected results and outcomes) and the validity of the 4th mid-/long-term plan (7 years from FY2022), according to the above-mentioned guidelines. The Committee concluded that the rationale behind the R&D programs, the relevance of the program outcome and the efficiency of the program implementation during the 3rd mid-/long-term plan are comprehensively evaluated as "A", and the R&D programs for the 4th mid-/long-term plan is generally appropriate. This report summarizes the results of the assessment by the Committee. In addition, the appendices of the report contain the responses from JAEA on the comments and suggestions by the Committee and the presentation materials submitted to the Committee.
Hashimoto, Makoto; Kinase, Sakae; Munakata, Masahiro; Murayama, Takashi; Takahashi, Masa; Takada, Chie; Okamoto, Akiko; Hayakawa, Tsuyoshi; Sukegawa, Masato; Kume, Nobuhide*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2020-071, 53 Pages, 2021/03
In the case of a nuclear accident or a radiological emergency, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), as a designated public corporation assigned in the Disaster Countermeasures Basic Act and the Armed Attack Situation Response Law, undertakes technical supports to the national government and local governments. The JAEA is requested to support to evaluate radiation doses to residents in a nuclear emergency, which is specified in the Basic Disaster Management Plan and the Nuclear Emergency Response Manual. For the dose evaluation, however, its strategy, target, method, structure and so on have not been determined either specifically or in detail. This report describes the results of investigation and consideration discussed in the "Working Group for Radiation Dose Evaluation at a Nuclear Emergency" established within the Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center to discuss technical supports for radiation dose evaluation to residents in the case of a nuclear emergency, and aims at contributing to specific and detailed discussion and activities in the future for the national government and local governments, also within the JAEA.
Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Kin, Tadahiro*; Iwamoto, Osamu
JAEA-Conf 2020-001, 236 Pages, 2020/12
The 2019 Symposium on Nuclear Data was held at Chikushi Campus Cooperation Building (C-Cube), Kyushu University, on November 28 to 30, 2019. The symposium was organized by the Nuclear Data Division of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan (AESJ) in cooperation with Sigma Investigative Advisory Committee of AESJ, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Kyushu Branch of AESJ, and Center for Accelerator and Beam Applied Science of Kyushu University. In the symposium, there were one tutorial, "From the resonance theory to statistical model", and five sessions, "Study on Nuclear Data and related topics", "Reactor physics", "International Cooperation", "Nuclear Physics", and "High Energy Nuclear Data and their Application". In addition, recent research progress on experiments, nuclear theory, evaluation, benchmark and applications was presented in the poster session. Among 85 participants, all presentations and following discussions were very active and fruitful. This report consists of total 42 papers including 13 oral and 29 poster presentations.
Sato, Tetsuro*; Ando, Masaki; Sato, Masako*; Saito, Kimiaki
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 210, p.105973_1 - 105973_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:35.81(Environmental Sciences)A method was devised for estimation of external doses of Fukushima residents expected to return to their homes after evacuation orders are lifted. 211 residents expected to return to six towns and villages were surveyed in FY 2014, FY 2015, and FY2016. Interviewing returning residents about their expected life patterns after returning, air dose rate were measured along the reported personal trails representing their patterns of movement in daily life. Excluding 15 residents from whose homes we were unable to take air dose rate measurements, the maximum external effective dose and the average external effective dose were estimated respectively as 4.9 mSv/y and 0.86 mSv/y. Although the mean values and dispersion of external effective doses differ depending on the evacuation level, for 93.3% of all residents, the estimated external effective doses were less than 2 mSv/y. The average exposure dose at home accounts for 66.8% of the annual exposure dose.
Chiba, Satoshi*; Ishizuka, Chikako*; Tsubakihara, Kosuke*; Iwamoto, Osamu
JAEA-Conf 2019-001, 203 Pages, 2019/11
The 2018 Symposium on Nuclear Data was held at Multi-Purpose Digital Hall and Collaboration Room of Tokyo Institute of Technology, on November 29 and 30, 2018. The symposium was organized by the Nuclear Data Division of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan (AESJ) in cooperation with Sigma Special Committee of AESJ, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, and Laboratory for Advanced Nuclear Energy of Institute of Innovative Research, Tokyo Institute of Technology. In the symposium, there were one tutorial, "Development of nuclear data processing code FRENDY", one special lecture "What the future holds for Nuclear Energy" and seven oral sessions, "Nuclear Data and Future Perspectives", "Current Status and Future Perspectives of Reactor Physics", "Topics", "Nuclear Data Applications", "International Session", "Nuclear Data Measurements and New Technology for Nuclear Reactor Diagnosis", and "Data Needs from New Fields". In addition, recent research progress on experiments, evaluation, benchmark and application was presented in the poster session. Among 82 participants, all presentations and following discussions were very active and fruitful. This report consists of total 35 papers including 13 oral and 22 poster presentations.
Kurihara, Momo*; Yasutaka, Tetsuo*; Aono, Tatsuo*; Ashikawa, Nobuo*; Ebina, Hiroyuki*; Iijima, Takeshi*; Ishimaru, Kei*; Kanai, Ramon*; Karube, Jinichi*; Konnai, Yae*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 322(2), p.477 - 485, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:21.22(Chemistry, Analytical)We assessed the repeatability and reproducibility of methods for determining low dissolved radiocesium concentrations in freshwater in Fukushima. Twenty-one laboratories pre-concentrated three of 10 L samples by five different pre-concentration methods (prussian-blue-impregnated filter cartridges, coprecipitation with ammonium phosphomolybdate, evaporation, solid-phase extraction disks, and ion-exchange resin columns), and activity of radiocesium was measured. The z-scores for all of the  Cs results were within
Cs results were within  2, indicating that the methods were accurate. The relative standard deviations (RSDs) indicating the variability in the results from different laboratories were larger than the RSDs indicating the variability in the results from each separate laboratory.
2, indicating that the methods were accurate. The relative standard deviations (RSDs) indicating the variability in the results from different laboratories were larger than the RSDs indicating the variability in the results from each separate laboratory.
Yoshizawa, Atsufumi*; Oba, Kyoko; Kitamura, Masaharu*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 18(2), p.55 - 68, 2019/06
This study aims to improve the potential of an emergency response by analyzing the workload management during the accident at the Emergency Response Center (ERC) of TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. Specifically, the research focused on the response of the ERC during the time between the discontinuation of Unit 3 core water injection and its recovery. It identified the different types of workload at the ERC had and how they had been managed based on the record of a TV conference. It also deduced the casual factors of the responses, supplementing the interview record of the director of ERC at the time by applying workload management analysis. On the basis of these findings, lessons to enhance the potential of the on-site emergency response have been obtained for ERC and outside organizations.
Okumura, Keisuke; Riyana, E. S.
JAEA-Conf 2018-001, p.63 - 68, 2018/12
The decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) is an unexplored field. Although the investigations for inside primary containment vessel (PCV) by robots have been underway by IRID, actual situation inside the PCV and the characteristics of fuel debris have not been sufficiently clarified yet. Under such circumstances, the computational simulation with reliable data is an effective means for solving many problems for the 1F decommissioning. Here, as application examples using nuclear data such as JENDL-4.0, we will introduce some researches and developments on (1) prediction of dose rate distribution in PCV, (2) remotely operated vehicle (ROV) system to explore submerged fuel debris in PCV, (3) non-destructive assay of nuclear fuel materials in a fuel debris canister.
Saito, Kimiaki; Takahara, Shogo; Uezu, Yasuhiro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 60(2), p.111 - 115, 2018/02
, 60(2), p.111 - 115, 2018/02
no abstracts in English
Chadwick, M. B.*; Capote, R.*; Trkov, A.*; Herman, M. W.*; Brown, D. A.*; Hale, G. M.*; Kahler, A. C.*; Talou, P.*; Plompen, A. J.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 148, p.189 - 213, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:67 Percentile:98.13(Physics, Nuclear)The CIELO collaboration has studied neutron cross sections on nuclides that significantly impact criticality in nuclear facilities -  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Fe,
Fe,  O and
O and  H - with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality. This report summarizes our results and outlines plans for the next phase of this collaboration.
H - with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality. This report summarizes our results and outlines plans for the next phase of this collaboration.
Sanami, Toshiya*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Kunieda, Satoshi; Nakamura, Shoji
JAEA-Conf 2017-001, 222 Pages, 2018/01
The 2016 Symposium on Nuclear Data was held at Kobayashi Hall of High Energy Accelerator Research Organization, on November 17 and 18, 2016. The symposium was organized by the Nuclear Data Division of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan in cooperation with Radiation Science Center, High Energy Accelerator Research Organization, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency and North Kanto Branch of Atomic Energy Society of Japan. In the symposium, there were one tutorial, "Historical Evolution of Accelerators" and four oral sessions, "Overview of the ImPACT Program - Reduction and Resource Recycling of High Level Wastes through Nuclear Transmutation", "Facilities and experiments for nuclear data in Japan", "Nuclear data from measurement to application", and "Progress of neutron nuclear data measurement and research for its basics and application". In addition, recent research progress on experiments, evaluation, benchmark and application was presented in the poster session. Among 65 participants, all presentations and following discussions were very active and fruitful. This report consists of total 31 papers including 10 oral and 21 poster presentations.
Palmiotti, G.*; Salvatores, M.*; Yokoyama, Kenji; Ishikawa, Makoto
NEA/NSC/R(2016)6 (Internet), 42 Pages, 2017/05
Iwamoto, Osamu; Sanami, Toshiya*; Kunieda, Satoshi; Koura, Hiroyuki; Nakamura, Shoji
JAEA-Conf 2016-004, 247 Pages, 2016/09
The 2015 Symposium on Nuclear Data was held at Ibaraki Quantum Beam Research Center, on November 19 and 20, 2015. The symposium was organized by the Nuclear Data Division of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan in cooperation with Nuclear Science and Engineering Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency and North Kanto Branch of Atomic Energy Society of Japan. In the symposium, there were two tutorials, "Theory of Few-Body Systems and Recent Topics" and "Use of Covariance Data 2015" and four oral sessions, "Recent Research Topics", "Progress of AIMAC Project", "Present Status of JENDL Evaluated Files", and "Nuclear Data Applications". In addition, recent research progress on experiments, evaluation, benchmark and application was presented in a poster session. Among 99 participants, all presentations and following discussions were very active and fruitful. This report consists of total 46 papers including 13 oral and 33 poster presentations.
Aikawa, Masayuki*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ebata, Shuichiro*; Kunieda, Satoshi; Nakamura, Shoji; Koura, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Conf 2015-003, 332 Pages, 2016/03
The 2014 Symposium on Nuclear Data was held at Conference Hall, Hokkaido University, on November 27 and 28, 2014. The symposium was organized by the Nuclear Data Division of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan, Hokkaido Branch of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan, and Nuclear Reaction Data Centre, Faculty of Science, Hokkaido University in cooperation with Nuclear Science and Engineering Directorate of Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In the symposium, there were two tutorials, "Cross section measurement strategy for long lived fission product" and "Physics and Nuclear Data in Radiation Therapy" and four sessions, "A Neutron TOF Measurement Instrument desired by Nuclear Data Community", "Recent Topics", "Application of Nuclear Data", and "Nuclear Theory and Nuclear Data". In addition, recent research progress on experiments, evaluation, benchmark and application was presented in a poster session. Among 88 participants, all presentations and following discussions were very active and fruitful. This report consists of total 62 papers including 2 tutorials, 16 oral and 44 poster presentations.
 evaluation of F(
evaluation of F( -
- I)KCCYSL for targeting HER2
I)KCCYSL for targeting HER2Sasaki, Ichiro; Watanabe, Shigeki; Ohshima, Yasuhiro; Sugo, Yumi; Yamada, Keiichi*; Hanaoka, Hirofumi*; Ishioka, Noriko
Peptide Science 2015, p.243 - 246, 2016/03
Saito, Kimiaki; Kurihara, Osamu*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Takahara, Shogo; Sato, Tetsuro*
Radioisotopes, 65(2), p.93 - 112, 2016/02
Late information is introduced on dose evaluation due to external exposures which employ an important role in the exposures due to the Fukushima accident. First, merits and demerits of the currently used two methods, that is the estimation based air dose rates and the measurements using personal dosimeters, are discussed indicating some basic data after a fundamental concept of external dose evaluation is provided. Next, main activities are summarized on external dose measurements and evaluations after the accident. Finally, a new trial on dose evaluation in introduced.
Saito, Kimiaki
Radioisotopes, 63(11), p.515 - 517, 2014/11
no abstracts in English
 C control rod in severe accident of LWR
C control rod in severe accident of LWRShirasu, Noriko; Kurata, Masaki; Ogawa, Toru*
Proceedings of 2014 Water Reactor Fuel Performance Meeting/ Top Fuel / LWR Fuel Performance Meeting (WRFPM 2014) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2014/09
In the accident of Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, degraded fuels containing Zircaloy probably reacted with B C control blades containing stainless steel cladding or blade sheath. Since light elements like B and C are able to react easily with various elements and form various chemical species, several concerns are pointed out, such as variation in volatility and heat generation by oxidation of B and C. The chemical states of degraded fuel were evaluated on the assumption of thermodynamic equilibrium under various conditions of oxygen potential and temperature. The chemical behavior of B affects significantly the variation in oxygen potential with progressing severe accident, and many kinds of volatile compounds are formed by oxidation. The behavior of B causes the changes of volatility of FPs, such as Sr, Cs and Mo.
C control blades containing stainless steel cladding or blade sheath. Since light elements like B and C are able to react easily with various elements and form various chemical species, several concerns are pointed out, such as variation in volatility and heat generation by oxidation of B and C. The chemical states of degraded fuel were evaluated on the assumption of thermodynamic equilibrium under various conditions of oxygen potential and temperature. The chemical behavior of B affects significantly the variation in oxygen potential with progressing severe accident, and many kinds of volatile compounds are formed by oxidation. The behavior of B causes the changes of volatility of FPs, such as Sr, Cs and Mo.
Yanagisawa, Kazuaki
International Journal of Nuclear Knowledge Management, 2(2), p.91 - 104, 2006/00
Taking into consideration of national funds invested to individual research divisions in JAERI during the course of safety project studies, one found that a total input was approximately corresponded to 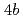 . Qualitatively, JAERI contributed to (1) the governmental policies, (2) the scientific technologies and scholarship, (3) the industries (technology transfer, patents, commissioned research etc.), (4) the local society in the lab location area, and (5) the international cooperation. Quantitatively, JAERI made the creation of added value (cost benefit), cost reduction and reduction of cost loss produced either in direct or indirect manner as research outputs. One found that a total output during the course of nuclear safety project study was approximately
. Qualitatively, JAERI contributed to (1) the governmental policies, (2) the scientific technologies and scholarship, (3) the industries (technology transfer, patents, commissioned research etc.), (4) the local society in the lab location area, and (5) the international cooperation. Quantitatively, JAERI made the creation of added value (cost benefit), cost reduction and reduction of cost loss produced either in direct or indirect manner as research outputs. One found that a total output during the course of nuclear safety project study was approximately 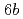 taking into consideration of nuclear market creation at electricity and facilities related to nuclear. This ex post evaluation tells that cost benefit made by nuclear safety project of JAERI is 1.5 (
taking into consideration of nuclear market creation at electricity and facilities related to nuclear. This ex post evaluation tells that cost benefit made by nuclear safety project of JAERI is 1.5 (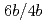 ) and such outcome contributes to the increase of general domestic products (GDP).
) and such outcome contributes to the increase of general domestic products (GDP).